- (+91) 22-69999644
- ecpinindia@gmail.com
Electromagnetic Regeneration Therapy
A non-invasive medical device
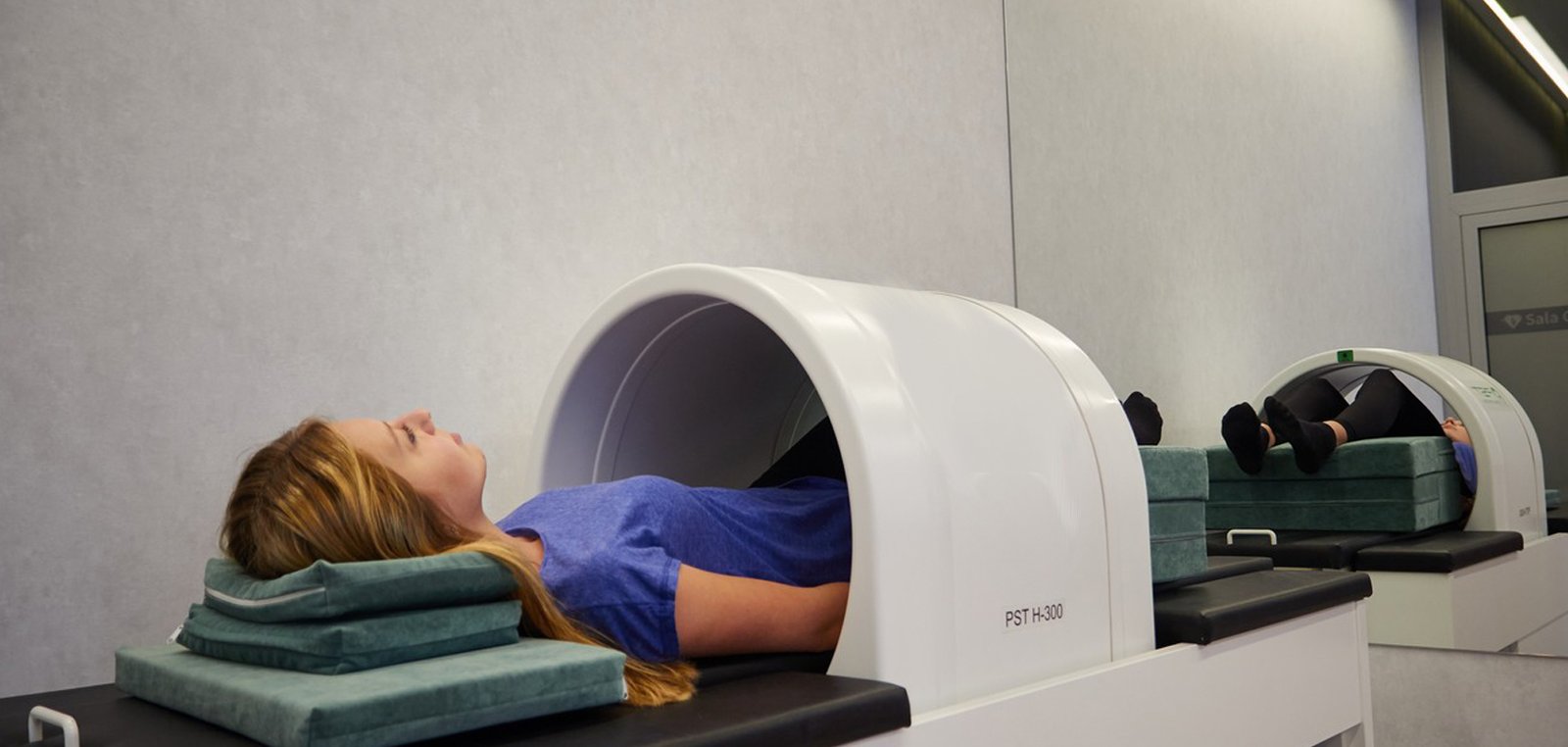
EMRT - Treatment
How Does It Work?


Research has shown that when stress is placed on a joint, a lower power electric signal is created. This natural signal tells the body to repair the damaged or worn tissue and to maintain the health and proper functioning of the joint. Sometimes, the signal is disturbed as a result of aging, injury or disease. When this happens, the body is unable to repair the damage itself. This results in pain, inflammation and loss of proper function in the joint.
 EMRT is unique in that it mimics the body’s natural signal, activating the normal healing process and stimulates the growth and repair of the damaged tissue.
EMRT has a success rate of 80-83% with patients experiencing significant improvement with the reduced pain and improved joint function.
EMRT is unique in that it mimics the body’s natural signal, activating the normal healing process and stimulates the growth and repair of the damaged tissue.
EMRT has a success rate of 80-83% with patients experiencing significant improvement with the reduced pain and improved joint function.
 EMRT has been used successfully all around the world by prominent professional athletes, amateur athletes, older people and patients who have had their quality of life compromised by arthritis, back pain, osteoporosis, sports type injuries and repetitive strain injuries. It is not relevant whether the patient is old or young or whether the defect is result of age, injury, chronic disease or inflammatory disease; EMRT is effective nonetheless View full list of treatable conditions.
EMRT has been used successfully all around the world by prominent professional athletes, amateur athletes, older people and patients who have had their quality of life compromised by arthritis, back pain, osteoporosis, sports type injuries and repetitive strain injuries. It is not relevant whether the patient is old or young or whether the defect is result of age, injury, chronic disease or inflammatory disease; EMRT is effective nonetheless View full list of treatable conditions.

Studies and the treatment of thousands of patients have shown that over 83% of patients experience a reduction in pain and inflammation, combined with an increase in physical function. Some patients find themselves free to all symptoms following the treatment. Others find their symptoms greatly reduced. Many patients are able to reduce or even discontinue their pain medication. Many have reported being able to return to normal routine activities and many are able to participate in their favourite sports.
The biggest benefit for many patients is that EMRT can save them the expense, pain and inherent risks of surgery.
What to expect during a treatment session?
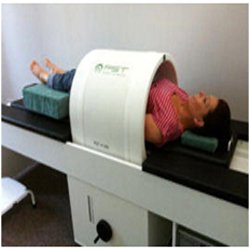
As EMRT is a non-invasive procedure, any type of clothing can be worn during treatment. The patient will or lie (depending on the area being treated) in a specially developed chair or bed. The joint or area to be treated is carefully positioned within the EMRT device. It is necessary to keep the area being treated completely still for the hour of treatment.
The procedure involves nine to twelve 01- hour treatments, conducted on consecutive days. If necessary, an interruption of less than two days (48 hrs) is authorised after completion of atleast 05 treatment sessions. It is also possible to do 02 treatments per day, as long as there is a break of atleast 04 hours between the end of the first treatment and start of the second one.
The regeneration process reaches its significant level approximately 8-12 weeks after the completion of the therapy sessions. The regeneration process may go on till a year.
Is the treatment painful?

The EMRT treatment session is completely non-invasive and most patients may feel a slightly tingling or sensation of warmth in the area that is being treated. Some may experience a temporary and slight increase in the normal pain that they feel in the affected joint. This is considered to be a positive reaction as it brought about by the reconstruction and healing that is occurring in the injured area.
• If the patient does feel discomfort, it usually passes quickly
• Some patients feel slight tingling sensation in the area being treated, or even warmth or cold.
• Some patients may also feel sensations in other joints or parts of the body, not directly being treated. As the signal travels in waveform throughout the body, it can be redirected to areas also needing attention, i.e. compensatory deficits.
Treatment restrictions
Because the signal is delivered through the device is of a very low range( one one-thousandth of energy of an MRI machine), EMRT is extremely safe. There have been no adverse side effects reported in the thousands of patients that have been treated worldwide. However, as an added precaution, based on ensuring the highest levels of safety, children, pregnant woman and people who have received treatment for cancer inn the past five years are not accepted for treatment.
Contradictions to EMRT:
• Patients with pacemaker
• Patients with ferrous implants
• Bacterial infections
• Severe cardiac insufficiency
• Suspected tumour or a diagnosed cancer requiring radiation and/or chemotherapy in the past 5 years
• Heavy bleeding
• Epilepsy
• Pregnant women
• Child under age the age of 10 years
Treatments to be avoided:
Treatments to be avoided during the EMRT treatment and in some cases, 6 weeks after • Intra articular injections • Invasive treatments • Manipulation of joint(chiropractic/osteopathic/physiotherapeutic measures, including traction table treatment and deep tissue massage)
EMRT treatable conditions
Degenerative disease:
• Arthritis of large (e.g. gonathritis, arthrosis of the knee) and small joints (e.g. spondylitis)
• Tendonitis/insertion tendinopathy (e.g. tennis elbow)
• Lumbago, degenerative disc disease, discopathy (e.g. lumbar disc protrusion)
• Calcaneal spur
• Deforming arthrosis of the hands
• Gonathritis, coxarthrosis, rhizomelic arthrosis of the thumb
Traumatic injuries:
• Ligament lesions/ruptures (e.g. cruciate ligament ruptures)
• Meniscus injuries
• Fractures (e.g. cartilage and bone fractures)
• Pseudo arthrosis (i.e. non-union at fracture site)
• Soft tissue injuries (e.g. whiplash)
• Indicated as a post-op treatment to sustain healing and improve functional rehabilitation.
Inflammatory disease:
• Rheumatic joint disease (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis)*
• Metabolic joint damage (e.g. gout)*
Deformities of the musculoskeletal system:
• Spinal column (e.g. scoliosis**)
• Foot (e.g. hallux valgus, hallux rigidus, splay foot, club foot, pes planus)
• Arthrosis of the hands
Joint chondromatosis:
• Cartilaginous changes within the synovial membrane of a joint Osteochondrosis
• Perthes disease
• Osteochondrosisdissecans
• Arthritis treatment
Treating arthritis with EMRT
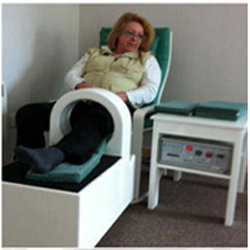
• While there are many forms of arthritis that can be treated by EMRT, one of the most common forms of arthritis that is responsive to EMRT is osteoarthritis (OA) or degenerative joint disease. OA is a condition that develops gradually, over several years. For some people, the changes are subtle and occur over such a long period of time that they are hardly noticeable. Others, However, may experience gradual worsening, including pain and restricted movement, particularly in large joints such as the hip or knee
• In a healthy joint, the layer or cartilage that covers the bone end is very strong, smooth and flexible. It absorbs the stress put on a joint and protects the bones from damage. In osteoarthritis, this becomes brittle, thin and pitted and over time, can wear out completely. When the cartilage deteriorates, the bone underneath thickens and broadens out. As the cartilage become thinner, the bones of the join rub together, causing pain, inflammation and the gradual build-up of bony outgrowths (osteophytes), which it look knobbly, also, the joint capsule becomes thicker and the amount of synovial (lubricating) fluid can increase, often causing the joint to swell. This can cause it to become stiff and painful.
• EMRT produces magnetic fields that stimulates chondrocytes (cartilage-producing cells) and fibroblasts (connective tissue producing cells) into regenerating their respective tissues. Tissue cultures of chondrocytes stimulated by EMRT have shown a markedly higher production of cartilage because of this, EMRT can reverse the changes in joint structure caused by arthritis and help to stabilie the joint’s synovial fluid. This will result in a further improvement in overall joint function.

• Joint degeneration (osteoarthritis) is the successive wearing away of the cartilage in the joints and generally developes over the course of many years and decades. In its advanced stages, the bones nearest to the joints, the synovial membranes, joint capsules and muscles undergo changes. This means osteoarthritis is not limited to cartilage, but can effect an entire joint.
There are now a range of treatments available for osteoarthritis, ranging from medication and physiotherapy to surgical interventions, as well as complementary therapies such as acupuncture. Most of the treatments are aimed at the symptoms such as pain, associated with this condition rather than addressing the cause-cartilage degeneration for which there are hardly any treatment as yet.
However, if detected in early time and treated properly, many of the consequences associated with osteoarthritis can be avoided. Although there are no treatments that can be universally applied or that are garuanteed to work.
1 in every 3 women and 1 in every 5 men in india above 50years of age suffer from osteoporosis. Currently, more women die from complications of osteoporotic fractures than from all cancers of the ovary, uterus and cervix combined, Osteoporosis means porous bones. It is a silent disease that is not usually diagnosed until a fracture occurs. Bone is a living tissue that is constantly being removed and replaced and as we get older, more bone is naturally lost than is replaced.
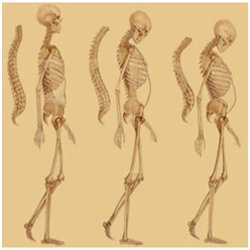 This causes bone to become fragile and break easily, e.g. through a bump or a fall. Also, if you have one low trauma fracture, this doubles your risk of another fracture due to osteoporosis.
This causes bone to become fragile and break easily, e.g. through a bump or a fall. Also, if you have one low trauma fracture, this doubles your risk of another fracture due to osteoporosis.
Osteopenia is the early stage of osteoporosis. Having osteopenia, places a person at the risk of developing osteoporosis. A diagnosis of osteopenia is a warning that you must start taking care of your bones and that prevention methods need to be put in place.
As a treatment for osteoporosis and osteopenia, EMRT is the natural alternative to medication. It is being applied for the first time in india to stimulate the rejuvenation of bone in patients.
This is done by re-stimulating osteoblast formation (bone forming cells) and this replaces the bone loss created by osteoporosis. This re-stimulation also retains proteoglycan & chondrocyte composition within the bones and also the cartilage between the bones. Therefore, post EMRT treatment ranges of movements in the spine and hips are greatly increased and postural height is restored – eliminating kyphosis of the upper back or the dowagers hump presentation.
EMRT treatment will result in the following:
• Increased bone density
• Increased bone quality
• Re-stimulation of osteoblast formation
• Reduction of pain
• Improved physical resilience
• Increased joint function
Sports injury treatment
 Treating sports injury and bone fracture with EMRT:
Treating sports injury and bone fracture with EMRT:
Tried and tested indications for the application of ELECTROMAGNETIC REGENERATION THERAPY are sports injuries. These injuries can be acute, one single event (e.g. acl tear in the knee) or chronic from overuse or repetition building up in the body for months or even years (e.g. Achilles tendonitis, impingement syndrome in the shoulder, tennis elbow). As a rule, sports are injury are usually healed in few weeks. But sometimes the pain persists, and the patient do not regain their initial articular activity in full. In these cases, EMRT will have beneficial effects on the evolution of the trauma.
The traditional approach for treatment of joints and connective tissue include:
• R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compress and Elevation)
• Splinting or demobilization of the affected are, e.g. crutches
• Over the counter or prescription anti-inflammatory drugs
• Physical therapy/ physiotherapy and exercise to bulk up the muscle around the joint to protect it
• Faradic and ultrasound modalities
• Corticosteroid injections
• And ultimately, surgery
 EMRT is a non-invasive alternative or an adjunct to surgery that stimulates the body to repair damaged tissue to speed up the healing procedures. In fact, we’ve had very positive experiences in the clinic with EMRT shortening the healing time 50%. As an example: a grade II ankle sprain that usually may take 3-4 weeks, has been brought right within 2 weeks. And this is a natural heal, with none of the harsh adverse side effects associated with injections and medications.
EMRT is a non-invasive alternative or an adjunct to surgery that stimulates the body to repair damaged tissue to speed up the healing procedures. In fact, we’ve had very positive experiences in the clinic with EMRT shortening the healing time 50%. As an example: a grade II ankle sprain that usually may take 3-4 weeks, has been brought right within 2 weeks. And this is a natural heal, with none of the harsh adverse side effects associated with injections and medications.
EMRT works with all types of connective tissue: bone, cartilage, ligament, tendon, blood, collagen, adipose (fatty tissue) and therefore speeds up the process of:
• Cartilage rejuvenation (knees, shoulder, hip)
• Cruciate (post-op) recovery
• Meniscus tears
• Ligament sprain/rupture
• Tendon damage/rupture
• Tendonitis (Achilles, tennis elbow, golfers elbow, shoulder tendonitis)
• Rotator cuff damage
• Impingement syndromes in the shoulder
• Dislocations/relocation of joints
• Muscular tear/ scar tissue damage
• Bone strengthening
• Mal-union of fractures
• Micro-fractures (pre/post-surgery)
Note: During and after EMRT sessions, there is no need of physiotherapy or physical treatment. This in fact replaces it. Follow ups at the EMRT clinic are required and we provide all exercise and rehabilitation programs. If you live some distance away, we can tie in with your physio there for continuity.
New medical applications and additional Indications
The following indications have also been successfully treated:
• Anterior cruciate repair and rehabilitation
• Osteoporosis
• Carpel tunnel syndrome
• Tendonitis
• Fresh bone fractures and stress fractures
• Aseptic necrosis or avascular necrosis
• Fibromyalgia
• Sciatic nerve pain
• Delayed poliomyelitis syndrome (sequelae)
• Meta-tarsalgia
• Morton’s neuroma
• Atrophy of the plantar metatarsal fat pad
• Plantar fasciitis
• Acute burns
• Immuno-deficient disorders
• Epilepsy non-responsive to medication
• Diabetic neuropathy
• Migraine headaches
• Ankylosing spondylitis
• Spondylolisthesis and herniated discs
• Hemopheliac
• Dupuytren’s contracture